One of the benefits of the increasing adoption of robotics and automation for fill-finish processing is that with growth comes standardization and accessibility. There has been a confluence of focus and interest in small-scale aseptic processing solutions, preceded by market trends in drug discovery, patient-centered medicine, and compounded pharmaceutical products. Other trends like decentralized manufacturing, point-of-care manufacturing, and advancements in modular solutions for fill-finish have coincided as avenues to address these growing segments of the industry. With advanced automated technology more available, the pharmaceutical industry is approaching the drug development lifecycle more holistically, as automated and data solutions address key operational friction points in areas like project scaling, validation, and technology transfer.
Still, professionals in drug research and development or direct-to-patient applications like compound pharmacies, may hesitate when deciding whether or not to adopt advanced solutions. Is it cost-effective for smaller operations, startups, and new/potential products in the early stage of development? Does the design of the automation lend itself to ease of training, or is there a steep learning curve? And what advantages do robotics and automation offer for both the process and operator over manual setups?
The Benefits of Modular Fill-Finish Technology
Cost – While the initial startup cost can be a deterrent, as advanced solutions have become more common, they’ve also become more cost-effective. The technological and design advancements in aseptic processing technologies have made them more efficient, intuitive, and effective; the quality and function of these solutions are so refined that advancements in user experience and accessibility are being made in strides. Additionally, while start-up costs may be more when compared to manual solutions, the overall cost-of-ownership savings offered by an aseptic processing system is substantially more over both the drug development lifecycle and the total life of an operation. Fill-finish tools are now flexible and scalable, able to adapt to the scope of operation. Being able to use the same set of tools throughout the drug development process saves significant investment in re-validation and re-training.
Personnel and training – Qualified and trained personnel are essential in running any aseptic processing operation. An important consideration when exploring automated solutions is the ease of training and operation, and the technical resources available to staff for any educational and troubleshooting needs. Some fill-finish setups may have different operating systems for various technologies (i.e. distinct HMIs for barrier and filling line technology), while more integrated solutions leverage a single, centralized HMI across all systems. This approach reduces the scope of training and removes significant obstacles in cross-system integration.
Advanced solutions also offer a safer environment for personnel at every size of operation. A recent study comparing1 the use of robotics to manual operations not only found advancements in efficiency and preparation time but that robotic operations showed clear risk reduction (on average, two high and two moderate-risk operations when done manually versus four low-risk operations when done robotically). Additionally, strain-related injuries saw a statistically significant reduction when robotics were used.
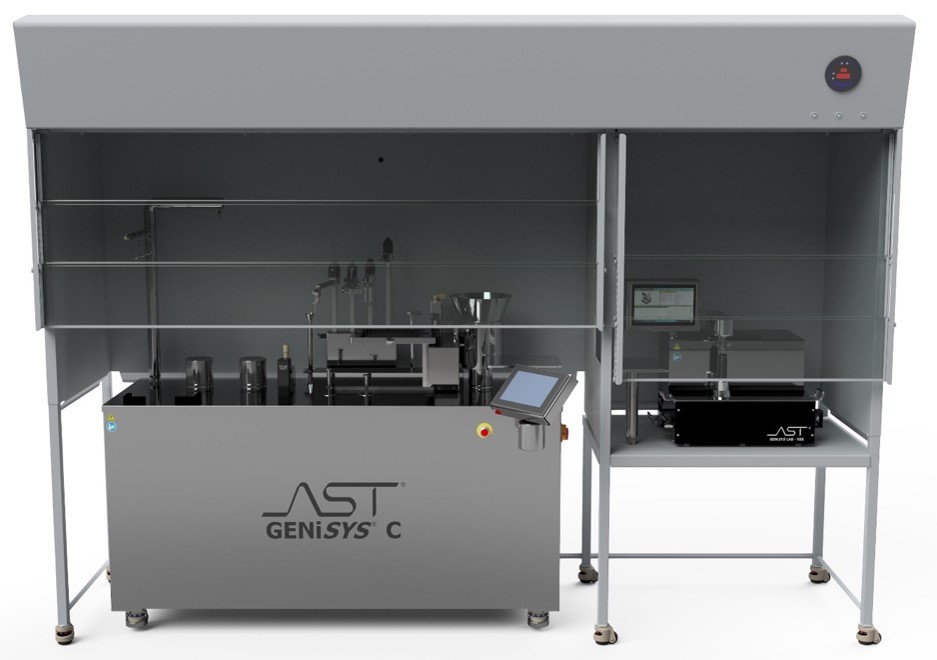

Figure 1. The GENiSYS C Cart and GENiSYS Lab Vial Sealing System (VSS) are two compact solutions for small or decentralized operations.
Process and Operational Efficiencies – When compared to manual operations, robotics and automation offer advanced solutions that address dose accuracy, product handling, and product quality by utilizing a wide range of process controls and redundancies. Zero-waste strategies can be put in place for highly valuable or sensitive products in the earliest stages of development and carried on through to commercial production. Product protection is also significantly improved as robotics de-risk operations by reducing human interventions. Additionally, automated systems can offer comprehensive data recording that’s incorruptible, an important consideration for those looking to improve their data integrity practices.
With these advancements in automation and robotics, high standards of quality are the expectation across varying manufacturing contexts with regulatory thresholds. Projects with a smaller footprint, whether R&D, process development, startups, or compounding operations, have access to powerful modular technology that enables robust and repeatable product quality.
Reach out to one of our team members today for an in-depth walk-through of our advanced aseptic processing solutions for smaller footprints.