Research and development is a critical undertaking for pharmaceutical manufacturers and is the backbone of the life sciences industry. Every lifesaving and life-improving treatment that has ever been produced started in a laboratory setting. Before a treatment can reach a patient in need, it’s in the laboratory that it’s discovered, refined, and then pushed forward to start its pre-clinical to commercial journey. A recent comprehensive overview of pharmaceutical investments found that research and development expenditures play a larger role than previously thought throughout the industry. A recent revaluation of 2021 Research and development spending had it at $276 billion, exceeding twice the amount cited in previous estimates, with total associated costs per successful drug approval at more than $5 billion per product commercialization.
With such a prominent commitment necessary, a question drug developers frequently revisit is what ways are available to make R&D more efficient and effective. Automation is one avenue that continues to grow in application and potential for drug discovery and development. As important as research and development is, many laboratory settings still use primarily manual methods. And though manual methods can be useful in addressing the variations inherent in the R&D process, the inefficiencies and obstacles associated with a manual-only approach are well defined, including:
- Human error – The more manual the process, the more likely the process will encounter mistakes in operation, protocol, or record-keeping.
- Imprecise operations that vary in the slightest can often go unnoticed by the operator but have consequences on quality and data.
- Contamination risk – Human beings are demonstrably the largest source of contamination in an aseptic processing setting. Filling by hand is a high-risk operation that can be de-risked by the right automated solution.
- Data integrity risks – Manual record keeping, whether done digitally or on paper, is highly prone to errors or incomplete information that can compromise downstream developmental milestones and technology transfer. Risks to data integrity continue to be an industry-wide issue that was spotlighted in a recent 15-year trend analysis of the FDA warning letters.
Automated lab technology provides clear improvements and advancements in each of these areas and can offer additional efficacy for the entire drug development lifecycle.
Asking the Right Questions of Your R&D Automation
In the initial planning phases, it’s crucial to examine the automated solutions available to ensure alignment with the project scope. Important questions include:
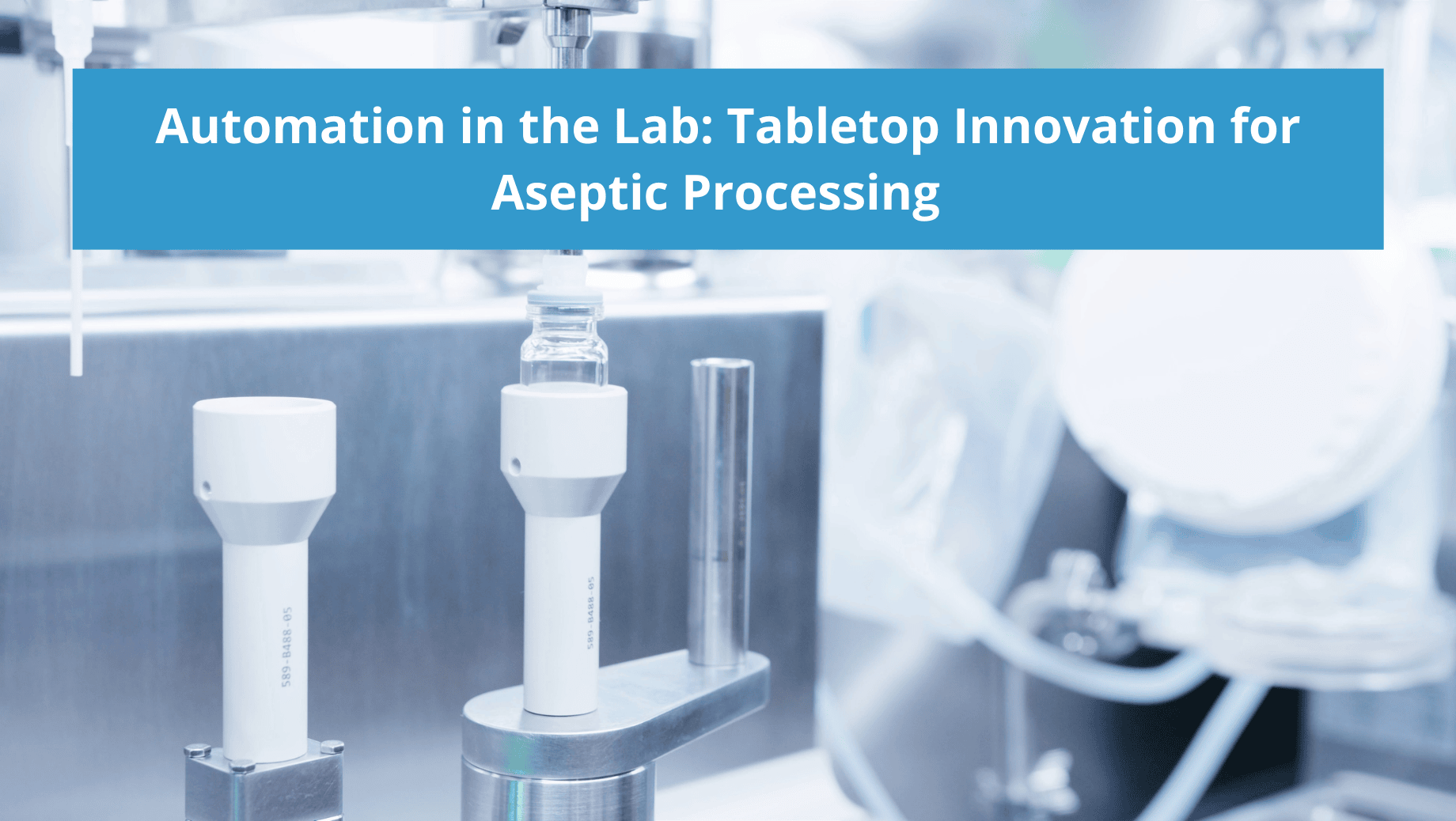
- Is the automated solution compact? – Laboratory settings are conventionally smaller spaces requiring newer technology that’s able to assimilate and retrofit into existing operational parameters. A common question is whether automated systems have a small enough footprint to fit into a benchtop operation or if the system would require additional space. Utilizing a system designed for tabletop processing is a key consideration when automating R&D.
- Is it efficient and effective? The benefit of implementing automation should be both an immediate and long-term improvement in the efficiency and effectiveness of aseptic processing. This can be achieved with technology that’s highly repeatable, and that can increase throughput when compared to manual processes. This leads to more available data with less variability. Additionally, technologies that are demonstrably effective in the R&D phase should be available in larger, more advanced solutions applicable for the later stages of drug development. The result is clear cost and time savings over the life of an operation.
- Is it compatible with the R&D process? Research and developmentrequires the ability to investigate and experiment with processes and outcomes. A common hesitation with automation is whether a system will be too limited or rigid in design when it comes to process or recipe changes. Flexible automation that is configurable to the operation’s scope can empower the operator to follow the data wherever it leads.
- Will the technology last? A natural concern with advanced technology is how long it will be supported before becoming obsolete. If you’re making a substantial investment in automated technology, it should come with the peace of mind that it’s built to last and will be supported throughout the life of the equipment. Additionally, it should tested and proven for the type of product being processed and the associated workload.
An Advanced Benchtop Solution
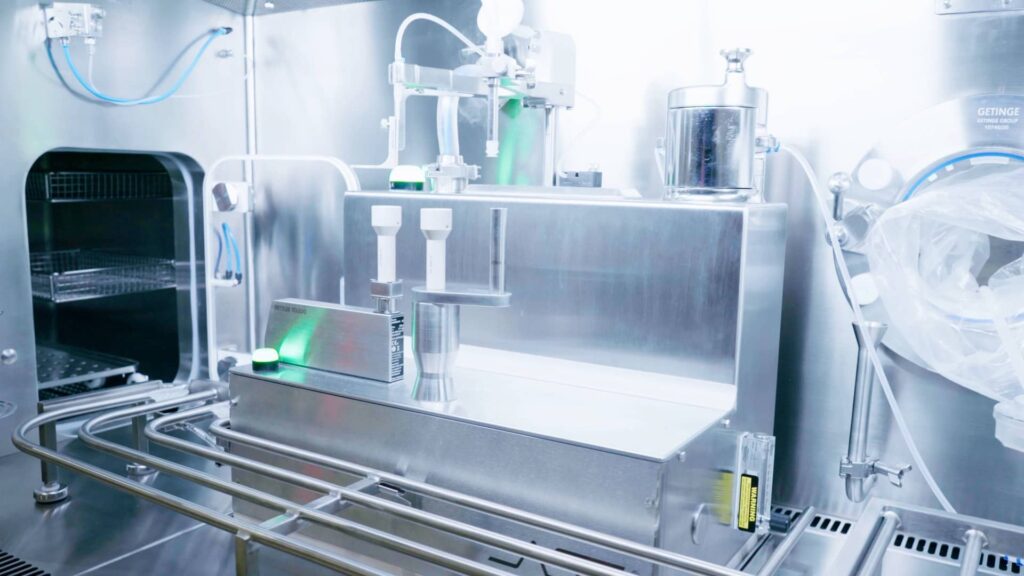

Figure 1. The Container Filling System (CFS) uses precise, servo-driven filling and closing technology.
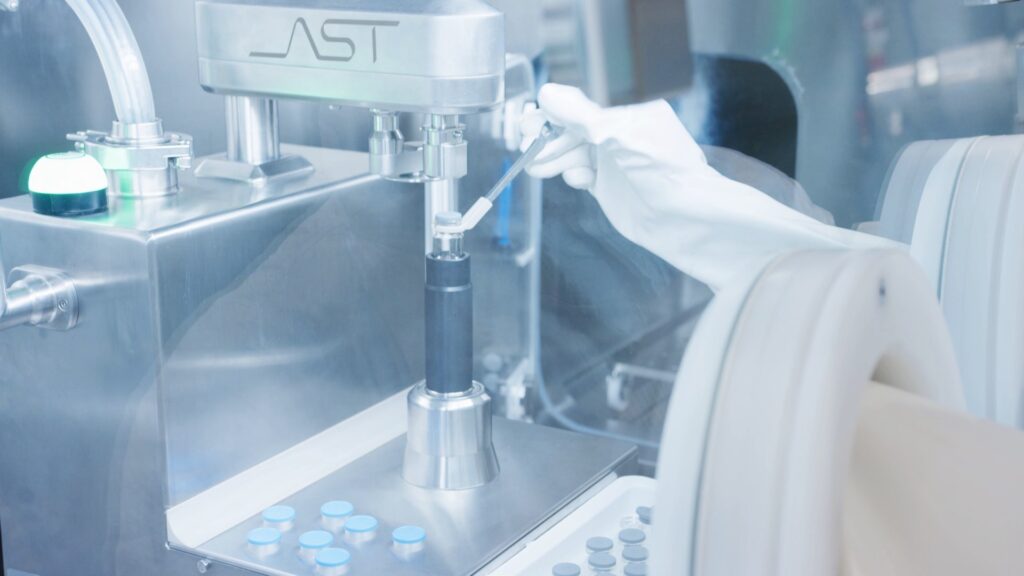

Figure 2. The Vial Sealing System (VSS) offers an aesthetic pharmaceutical-grade seal utilizing a spinning disk.
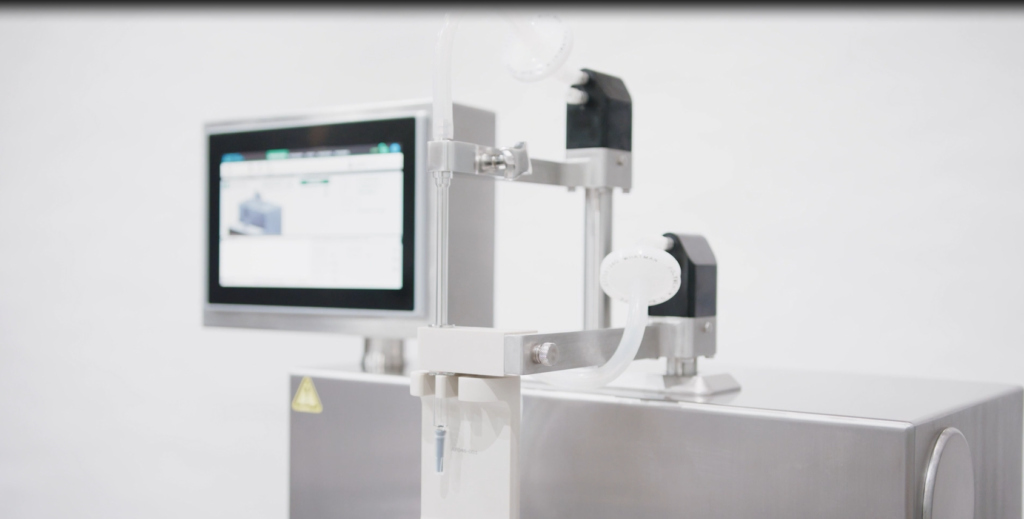

Figure 3. The Containers Closing System (CCS) performs precise piston placement using vacuum, vent tube, or combination stoppering methods.
AST’s GENiSYS Lab series offers automated, flexible aseptic processing (container filling, container closing, and vial sealing). The key advantage of these systems is that they were designed specifically for laboratory settings, configured with a tabletop technology that leverages precise automation for critical points in aseptic operation to lower overall risk and ensure the highest standards of product quality and data integrity from the very start of drug development. Each lab system is outfitted with an intuitive HMI for centralized control of the operation, process parameters, and records and utilizes flexible recipe-driven production to meet the full scope of research and development. End-to-end process data collection is accurate, automated, and exportable. Additionally, each system can be upgraded with an Electronic Batch Record (EBR) system to provide 21 CFR Part 11 compliance. As with all of AST’s solutions, each lab system is backed by a dedicated Customer Care team committed to the high performance of our equipment as long as it’s in the field.
Today’s R&D project is tomorrow’s breakthrough treatment. Reach out to one of our team members today for an in-depth walk-through of AST’s GENiSYS Lab series.